Parsing with AMF
AMF can parse AML dialects and the following API specifications:
The following section explains the basics of parsing, and the example shows how to parse each specification in Java or JavaScript.
Parsing Basics
Parsing is the process of analyzing a sequence of tokens and then building a data structure from them.
AMF uses SYAML to read a JSON or YAML file and generates an abstract syntax tree (AST) from the file, which is later used to generate a graph that represents the model. The model can be either a Web API model (representing an API, independent of its specification), or an AML document model (a dialect, vocabulary, or dialect instance).
Parsing returns a BaseUnit object, which is a graph of the model. Depending on the content in the parsed file, the BaseUnit object can be a Fragment, a Module, a Document or another type.
For more information about the AMF model, see the AMF model documentation resource.
The following figure shows the parsing process:
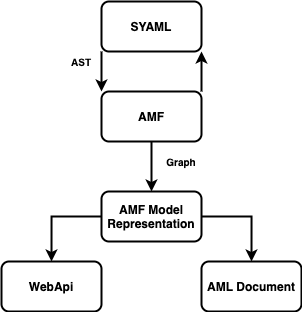
- SYAML is used to generate an AST from a YAML/JSON file
- AMF uses the AST to generate a graph of the model, called BaseUnit
- This model will be used in the following stages of AMF (resolution, validation, emission)
Parsing code examples
The file paths you give the parser must have the following structure:
Windows:
- Absolute path:
file:///C:/testing/api.raml - Relative path:
file://api.raml
MacOS and Unix:
- Absolute path:
file:///Users/aml/testing/api.raml - Relative path:
file://api.raml
Also, before parsing an AML dialect instance, you must register the dialect using the AMF.registerDialect() function.
- Java
- JavaScript
Code extracted from the examples GitHub repository.
Code extracted from the examples GitHub repository.